Microfinance in emerging markets has proven to be a uniquely stable investment. This niche asset class entails the provision of small loans and financial services to underserved entrepreneurs. It has demonstrated a remarkable stability, even during global downturns. Below, we explore three reasons why microfinance in emerging economies is a resilient and attractive investment, and how it delivers not just financial returns but also meaningful social benefits.
1. Microfinance: Stable returns through diversification
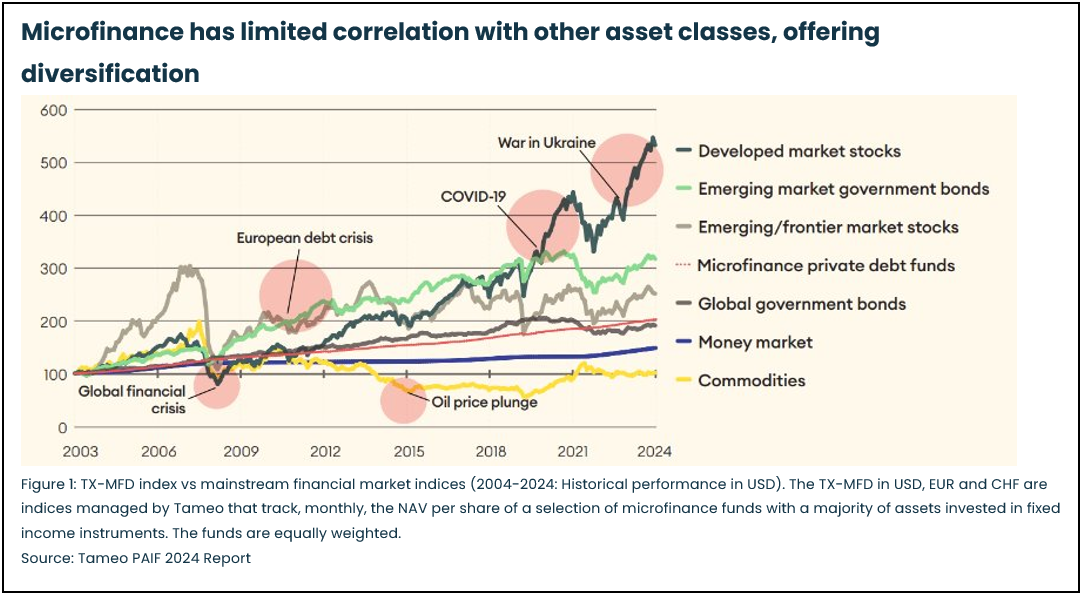
A key strength of microfinance investments is their independence from global financial markets. Microfinance institutions offer surprisingly stable returns because they are built on thousands of uncorrelated local businesses. By issuing financial services to local entrepreneurs, farmers, and shopkeepers who operate within local markets rather than international trade, microfinance portfolios have a limited correlation with global financial markets. These micro, small and medium enterprises (MSMEs), provide domestic goods and services in their local markets where demand remains stable regardless of global economic fluctuations.[1] These final beneficiaries depend on small yet resilient businesses, which is reflected in consistent and strong loan repayment rates. The result is low volatility: even during the peak phases of crises, microfinance yields did not rise above the +/- 1% mark.[2] Therefore, adding microfinance can significantly reduce overall portfolio risk and ensure further diversification. Moreover, a growing share of MFIs now operate under national banking supervision, providing investors with additional layers of oversight and risk management.
Although microfinance operates in developing and volatile regions and serves low-income clients, its low correlation with global markets and high loan repayment rates support stable investments. However, it is important to acknowledge that microfinance investments are not without challenges. Factors such as currency devaluation, political country-risk, regulatory changes, and the potential for borrower over-indebtedness can impact returns and add complexity, particularly in these emerging regions. Despite these risks, the sector’s low correlation with global markets and historically high loan repayment rates continue to support its reputation as a stable investment option.
2. Emerging markets: Stronger economic foundations boost stability
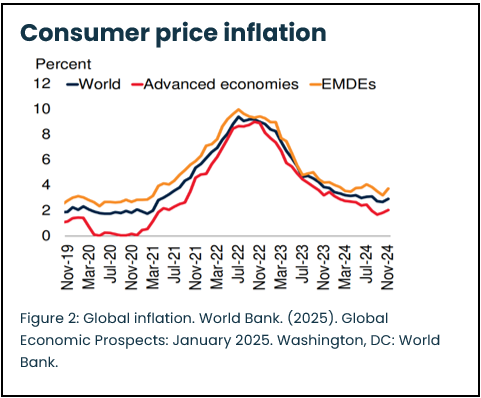
Declining global inflation, strong foreign reserves in emerging markings, and prudent practices of Microfinance Institutions (MFIs), contribute to the ongoing stability and resilience of microfinance investments. Inflation rates in emerging and developing economies have decreased and are projected to continue declining; with global average inflation at 5.9% in 2024, and forecasts indicating a further reduction to 5.3% in 2025 and 4.6% in 2026. [3]
At the same time, many emerging nations have bolstered their financial resilience by building high foreign currency reserves, which serve as buffers against external financial volatility. For example, foreign exchange reserves in emerging markets reached $698 billion in India, $350 billion in Brazil, and $41 billion in Nigeria[4]. More stable prices and steadier exchange rates allow MFIs to repay their loans with fewer uncertainties and currency fluctuations.
Besides this, MFIs have adapted to sector needs over the past 50 years, with the digitization of microfinance, such as mobile banking and AI-based credit scoring, which are now transforming the industry. MFIs have also responded to higher global interest rates by reducing foreign-currency borrowing and increasing local funding sources such as local deposits and bonds. This approach has further reduced currency risk on their balance sheets. The MFIs also receive technical support from development organizations and impact investors to strengthen their governance and manage risk. Emerging markets are diverse, and together with stronger balance sheets and prudent MFI management, this supports the steady performance of microfinance investments in these regions.
3. Beyond financial returns: Investing for impact
Beyond steady financial returns, microfinance investments generate measurable social impact, strengthening communities and livelihoods. Every dollar invested in microfinance aims for a financial return while directly improving the lives of the end beneficiaries. Borrowers often use these micro-loans to expand a small business, buy productive assets, or support their children’s education, which in turn boosts the household’s income and stability. Notably, up to 89% of microfinance clients have reported an improved quality of life, while 71% of clients increased their household savings, further contributing to greater financial security.[5] Many MFIs also provide basic financial literacy and business training alongside loans, so clients learn to budget and manage debt wisely, allowing them to further strengthen their resilience. Approximately 84% of microfinance clients experienced growth in their enterprises as a result of receiving these loans and services.[5] These positive outcomes are also visible within the communities, creating jobs and stimulating the local economy.
Case Study: Financiera FDL, Nicaragua – Enabling climate resilience*
Nicaragua faces high climate risks due to its geography and economy. Deforestation in rural areas causes soil degradation, pollution, and water issues, impacting small farmers who lack resources and knowledge for climate resilience. Financiera FDL, Nicaragua’s largest regulated MFI, offers green loans and technical assistance for climate mitigation and adaptation to 45,000 rural clients. A few key targets of FDL’s “Green Finance in Climate Change Mitigation and Adaptation” project, include ensuring that 6000+ farmers adopt climate adaptation measures, and creating a green portfolio with USD 2.4 million in green products by 2026.

* Financiera FDL is an investee of Incofin’s Climate-Smart Microfinance Fund (ICMF). Through ICMF, Incofin provided a senior loan of USD 2 million to Financiera FDL, allowing the investee to scale its green portfolio and develop these initiatives for climate mitigation and adaptation.
At Incofin, this blend of return and impact has been the driving philosophy from day one. Since its inception, Incofin has invested in 493 microfinance institutions across 76 emerging markets, focusing on increasing financial access, supporting smallholder agriculture, and expanding access to safe drinking water. Today, with USD 1.1 billion in assets under management, our debt, equity, and technical assistance programs reach more that 32 million micro-entrepreneurs who benefit from responsible financial services. By empowering these investees, Incofin’s investments help increase incomes, improve food security, and enhance the resilience of communities, while driving consistent performance for investors. In an era where investors are seeking both stability and purpose, microfinance in emerging markets has firmly established itself as a stable asset class with impact, delivering on both financial and social dividends.
References
[1] Enabling Microfinance. (n.d.). Microfinance: Unexpected stability in unstable times. Available at: https://enabling.ch/news/microfinance-unexpected-stability-in-unstable-times
[2] Invest in Visions. (n.d.). Diversification effects of microfinance investments. Available at: https://www.investinvisions.com/en/blog/press-releases/diversification-effects-of-microfinance-investments/
[3] International Monetary Fund (IMF). (2025). World Economic Outlook: April 2025. Available at: https://www.imf.org/en/Publications/WEO/Issues/2025/04/22/world-economic-outlook-april.
[4] World Bank. (2025). Global Economic Prospects: January 2025. Washington, DC: World Bank.
[5] 60 Decibels. (2025). Microfinance (MFI) Index.

Article by Sheryl Pluym, Business Analyst, Investor Solutions, Incofin Investment Management
